Explain diagram the antigen antibody reaction
Home » Background » Explain diagram the antigen antibody reactionYour Explain diagram the antigen antibody reaction images are ready. Explain diagram the antigen antibody reaction are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Explain diagram the antigen antibody reaction files here. Get all free images.
If you’re looking for explain diagram the antigen antibody reaction images information connected with to the explain diagram the antigen antibody reaction topic, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Explain Diagram The Antigen Antibody Reaction. Clumping of RBC due to antigen-antibody rxn. Blood-group aserythrocyte surface antigens whose antigenic differences determine blood groups. Because an antibody fits precisely with an antigen an antibody that binds to one antigen cannot bind to another antigen. Antigen Antibody Reaction Agglutination is defined as the formation of clumps of cells or inert particles by specific antibodies to surface antigenic components direct agglutination or to antigenic components adsorbed or chemically coupled to red cells or inert particles passive hemagglutination and passive agglutination respectively.
 Antigen Antibody Reactions Armstrong 2008 Isbt Science Series Wiley Online Library From onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Antigen Antibody Reactions Armstrong 2008 Isbt Science Series Wiley Online Library From onlinelibrary.wiley.com
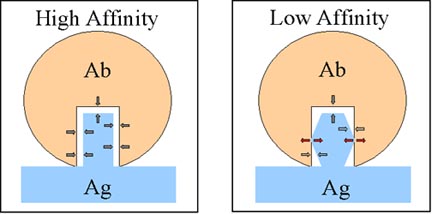
Antigen-antibody complexes form only after the nuclear contents of a cell are released into the bloodstream during the normal course of cell death or as a result of inflammation. Avidity is the strength of multiple interactions between antigen and antibody with multiple binding sites. Antigen-antibody reactionthe reversible binding of antigen to homologous antibody by the formation of weak bonds between antigenic determinants on antigen molecules and antigen binding sites on immunoglobulin molecules. Such assays called particle agglutination PA are based on the ability of sera containing HIV antibodies to crosslink small particles containing HIV antigens on the surface. It is a Y shaped molecule which is basically a protein that is produced by the B cells of the immune system. An antibody has a paratope that can recognize the epitope that is present on the surface of the antigen.
Antibody can inactivate the invading agent in.
The preferred sensor for detecting selected antigen-antibody reactions comprises a tube shaped reaction chamber for mixing a preselected amount of a pH adjusted aqueous solution to be tested with an antibody a heater for increasing a speed of an antigen-antibody reaction of the pH adjusted aqueous solution and the antibody a first sensor affixed to the. X-Ray crystallography studies of antigen-antibody interactions show that the antigenic determinant nestles in a cleft formed by the combining site of the antibody as illustrated in Figure 1. PA has advantages of sensitivity and relatively high inherent specificity because. Antigen-antibody complexes form only after the nuclear contents of a cell are released into the bloodstream during the normal course of cell death or as a result of inflammation. Aggregation of cells due to antibody binding is known as Agglutination. For instance lipids and all low-molecular-weight.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Thus our concept of antigen-antibody reactions is one of a key ie. Invading microorganisms have antigens. The antigen-antibody reactions that are used most in blood banking are known as hemagglutination ie they cause the agglutination of red cells. ELISA also known as an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is a biochemical. The noncovalent interactions that form the basis of antigen -antibody Ag-Ab binding include hydrogen bonds ionicbonds hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals interactions.
 Source: microbiologybook.org
Source: microbiologybook.org
The antigen-antibody reaction is widely used in laboratory diagnostics including immunohaematology. Laboratory tests to detect antibodies and antigens outside of the body eg in a test tube are called in vitro assays. All immunogens are also antigens because they react with corresponding antibodies see illustration. However an antigen may not be able to induce the formation of an antibody and therefore may not be an immunogen. But we know that some antibodies IgM and IgA exist in secreted form as a multi-antibody complex.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
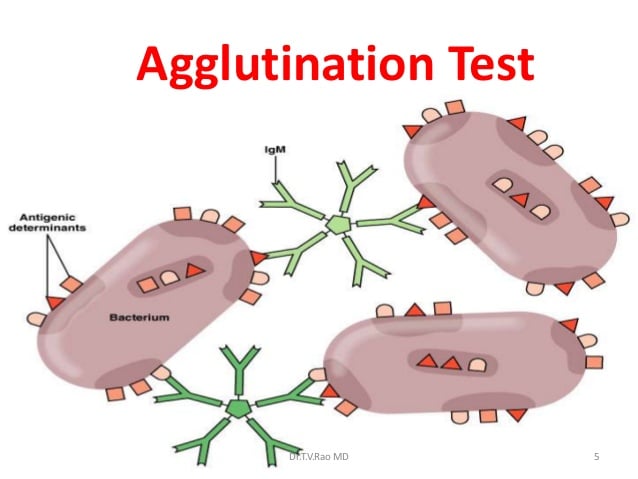
But we know that some antibodies IgM and IgA exist in secreted form as a multi-antibody complex. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign. 8 are highly specific and both fit into each other like a lock and key. When this involves red blood cells it is called haemolysis and causes the release of haemoglobin. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination.
 Source: microbenotes.com
Source: microbenotes.com
Laboratory tests to detect antibodies and antigens outside of the body eg in a test tube are called in vitro assays. Clumping of RBC due to antigen-antibody rxn. The antigen- antibody interaction is bimolecular irreversible association between antigen and antibody. Antigen-antibody reaction is the basis of humoral immunity or antibody mediated immune response. When this involves red blood cells it is called haemolysis and causes the release of haemoglobin.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
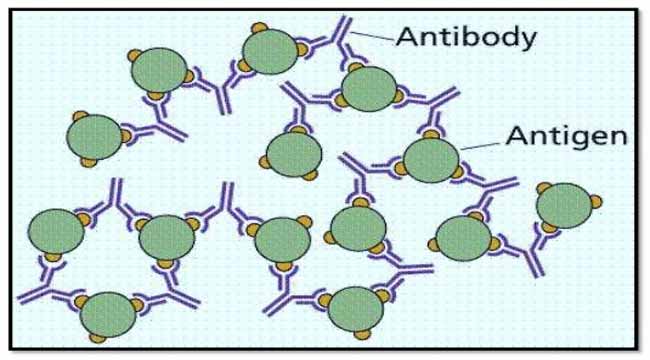
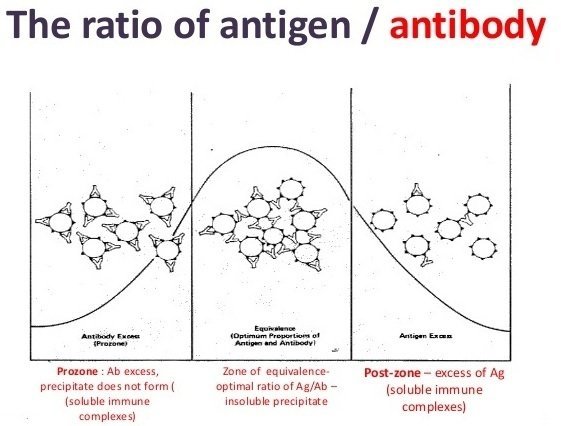
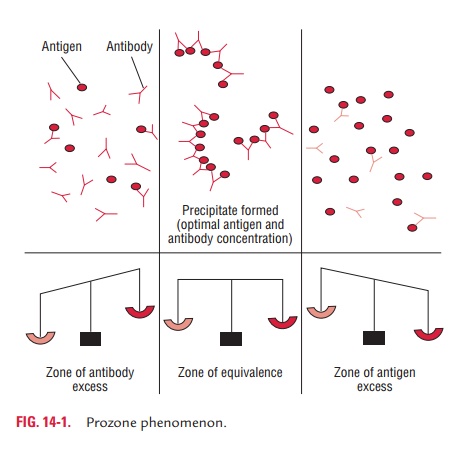
ELISA also known as an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is a biochemical. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign. An antibody has a paratope that can recognize the epitope that is present on the surface of the antigen. When both antibodies and their corresponding antigens are present in a solution we can often observe a precipitation reaction in which large complexes lattices form and settle out of solution. Thus the relationship between antigen concentrations as indi-cated by the antigenantibody complex formation and light scattering approaches linearity.
 Source: microbenotes.com
Source: microbenotes.com
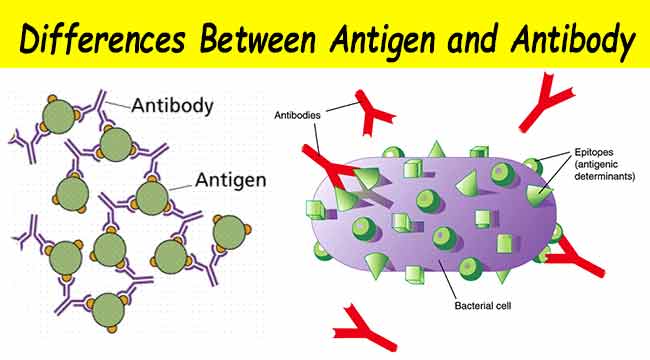
On their surface that the human body can recognise as being foreign - meaning not belonging to it. 8 are highly specific and both fit into each other like a lock and key. The mechanism of antigen-antibody reactions has been an attractive subject for experimentation and speculation ever since the early days of immunology. Such assays called particle agglutination PA are based on the ability of sera containing HIV antibodies to crosslink small particles containing HIV antigens on the surface. Antigen-antibody reaction is the basis of humoral immunity or antibody mediated immune response.
 Source: www2.hawaii.edu
Source: www2.hawaii.edu
Sometimes antigenantibody reactions result in lysis which is the breakdown or rupture of the cell membrane on which the epitopes or antigenic determinants are situated. The preferred sensor for detecting selected antigen-antibody reactions comprises a tube shaped reaction chamber for mixing a preselected amount of a pH adjusted aqueous solution to be tested with an antibody a heater for increasing a speed of an antigen-antibody reaction of the pH adjusted aqueous solution and the antibody a first sensor affixed to the. All immunogens are also antigens because they react with corresponding antibodies see illustration. Both the antigen and antibody act like a lock and key mechanism. Antigen-antibody reaction is the basis of humoral immunity or antibody mediated immune response.
 Source: biosciencenotes.com
Source: biosciencenotes.com
On their surface that the human body can recognise as being foreign - meaning not belonging to it. Such assays called particle agglutination PA are based on the ability of sera containing HIV antibodies to crosslink small particles containing HIV antigens on the surface. ELISA also known as an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is a biochemical. Process by which cells or other particles adhere to each other to form clumps. The mechanism of antigen-antibody reactions has been an attractive subject for experimentation and speculation ever since the early days of immunology.
 Source: microbiologyinfo.com
Source: microbiologyinfo.com
It is a Y shaped molecule which is basically a protein that is produced by the B cells of the immune system. Both the antigen and antibody act like a lock and key mechanism. ELISA also known as an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is a biochemical. Antigen Antibody Reaction Agglutination is defined as the formation of clumps of cells or inert particles by specific antibodies to surface antigenic components direct agglutination or to antigenic components adsorbed or chemically coupled to red cells or inert particles passive hemagglutination and passive agglutination respectively. Thus the relationship between antigen concentrations as indi-cated by the antigenantibody complex formation and light scattering approaches linearity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
An antibody has a paratope that can recognize the epitope that is present on the surface of the antigen. X-Ray crystallography studies of antigen-antibody interactions show that the antigenic determinant nestles in a cleft formed by the combining site of the antibody as illustrated in Figure 1. Clumping of RBC due to antigen-antibody rxn. The association between antigen and antibody includes various non-covalent interactions between epitope antigenic determinant and variable region VHVL domain of antibody. But we know that some antibodies IgM and IgA exist in secreted form as a multi-antibody complex.
 Source: www2.hawaii.edu
Source: www2.hawaii.edu
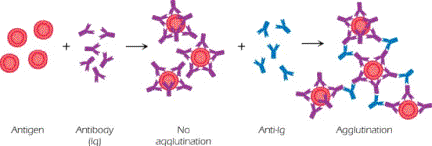
The word agglutination is derived from Latin word agglutinate means to glue to In humus binding of Abs pulls the antigen bearing cells close to each other resulting in the formation of clumps. On their surface that the human body can recognise as being foreign - meaning not belonging to it. The noncovalent interactions that form the basis of antigen -antibody Ag-Ab binding include hydrogen bonds ionicbonds hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals interactions. Because an antibody fits precisely with an antigen an antibody that binds to one antigen cannot bind to another antigen. Sometimes antigenantibody reactions result in lysis which is the breakdown or rupture of the cell membrane on which the epitopes or antigenic determinants are situated.
 Source: microbeonline.com
Source: microbeonline.com
All antibodies have at least two antigen binding sites represented as their Fab 2. PA has advantages of sensitivity and relatively high inherent specificity because. Clumping of visible complex and. When both antibodies and their corresponding antigens are present in a solution we can often observe a precipitation reaction in which large complexes lattices form and settle out of solution. It is a reversible chemical reaction.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Antigen antibody antigen- antibody complex 1 The forces joining the antigen-antibody complex are not strong covalent bonds but weaker bonds appropriately named weak interactions1. The antigen which fits into a lock ie. Antigen Antibody Reaction Agglutination is defined as the formation of clumps of cells or inert particles by specific antibodies to surface antigenic components direct agglutination or to antigenic components adsorbed or chemically coupled to red cells or inert particles passive hemagglutination and passive agglutination respectively. The antigen-antibody reaction is widely used in laboratory diagnostics including immunohaematology. On their surface that the human body can recognise as being foreign - meaning not belonging to it.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The word agglutination is derived from Latin word agglutinate means to glue to In humus binding of Abs pulls the antigen bearing cells close to each other resulting in the formation of clumps. HIV antigen-antibody reactions have been used to develop relatively rapid simple assays that do not require colorimetric readout. Sometimes antigenantibody reactions result in lysis which is the breakdown or rupture of the cell membrane on which the epitopes or antigenic determinants are situated. Clumping of visible complex and. Avidity is the strength of multiple interactions between antigen and antibody with multiple binding sites.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
It is a reversible chemical reaction. PA has advantages of sensitivity and relatively high inherent specificity because. Both the antigen and antibody act like a lock and key mechanism. Laboratory tests to detect antibodies and antigens outside of the body eg in a test tube are called in vitro assays. ELISA also known as an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is a biochemical.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Chemical Bonds Responsible for the AntigenAntibody Reaction. Antigen-antibody reaction is the basis of humoral immunity or antibody mediated immune response. When both antibodies and their corresponding antigens are present in a solution we can often observe a precipitation reaction in which large complexes lattices form and settle out of solution. Antigen-Antibody Reactions To bridge the gap between basic immunology and antibody detection methods Module 3 we will now briefly review the nature of antigen-antibody reactions. An antibody has a paratope that can recognize the epitope that is present on the surface of the antigen.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Chemical Bonds Responsible for the AntigenAntibody Reaction. The antigen- antibody interaction is bimolecular irreversible association between antigen and antibody. Antigen Antibody Reaction Agglutination is defined as the formation of clumps of cells or inert particles by specific antibodies to surface antigenic components direct agglutination or to antigenic components adsorbed or chemically coupled to red cells or inert particles passive hemagglutination and passive agglutination respectively. HIV antigen-antibody reactions have been used to develop relatively rapid simple assays that do not require colorimetric readout. 8 are highly specific and both fit into each other like a lock and key.
 Source: brainkart.com
Source: brainkart.com
Both the antigen and antibody act like a lock and key mechanism. It is a Y shaped molecule which is basically a protein that is produced by the B cells of the immune system. Sometimes antigenantibody reactions result in lysis which is the breakdown or rupture of the cell membrane on which the epitopes or antigenic determinants are situated. Types of Antigen Antibody ReactionThe types of antigen antibody reactions are Precipitation Reaction Agglutination Reaction Complement Fixation ELISA Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay Immunofluorescence. Antibody can inactivate the invading agent in.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title explain diagram the antigen antibody reaction by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.