Explain krebs cycle with diagram
Home » Wallpapers » Explain krebs cycle with diagramYour Explain krebs cycle with diagram images are available in this site. Explain krebs cycle with diagram are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Explain krebs cycle with diagram files here. Find and Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for explain krebs cycle with diagram pictures information related to the explain krebs cycle with diagram interest, you have come to the right site. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Explain Krebs Cycle With Diagram. Krebs Cycle is the second step of aerobic respiration in which pyruvate is oxidised completely into inorganic substances forming carbon dioxide. The Krebs cycle is simply another name for the Citric Acid Cycle so named for the researcher who identified the complete cycle in 1937. The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalysed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced which generate ATP in the electron transport chain. Every stage in each process is catalysed by a specific enzyme.
 A Different Design For The Krebs Cycle With Pyruvate As The Feeder Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
A Different Design For The Krebs Cycle With Pyruvate As The Feeder Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalysed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced which generate ATP in the electron transport chain. The specific enzymes of the Krebs cycle are all located on the inner walls of the cristae of mitochondria subcellular organelles. In the first step of the citric acid cycle acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. Krebs cycle was named after Hans Krebs who postulated the detailed cycle. The whole cycle of Kreb is described in the following figure. It involves the oxidative metabolism of acetyl units and serves as the main source of cellular energy mitochondria.
The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalysed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced which generate ATP in the electron transport chain.
The reactions which help in converting pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water in mitochondria are called the Krebs cycle. In the first reaction of the citric acid cycle acetyl CoA combines with the oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid. The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalysed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced which generate ATP in the electron transport chain. Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs cycle. Most of the released energy is converted into high energy bonds of ATP. Put more simply this means that bacteria do not have the cellular machinery for the Krebs cycle so it limited to plants animals and fungi.
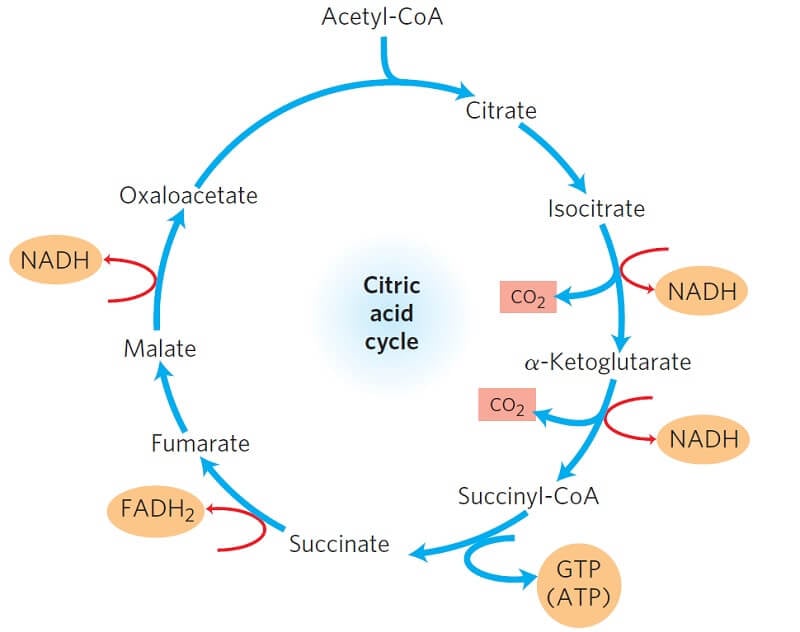 Source: microbenotes.com
Source: microbenotes.com
Krebs Cycle is the second step of aerobic respiration in which pyruvate is oxidised completely into inorganic substances forming carbon dioxide. In this article we will discuss about the functions of the Krebs cycle explained with the help of diagrams. It involves the oxidative metabolism of acetyl units and serves as the main source of cellular energy mitochondria. KREBS CYCLE MADE SIMPLE - TCA Cycle Carbohydrate Metabolism Made Easy - YouTube. In cell biology a mitochondrion plural mitochondria is a membrane-enclosed organelle often described as cellular power plants because they generate most of the ATP.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The flow diagram shows that every time a stage produces two hydrogen atoms in the presence of oxygen three ATP molecules are produced. This cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. In aerobic respiration both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle are involved whereas in anaerobic respiration only glycolysis takes place. The Krebs cycle named after 1953 Nobel Prize winner and physiologist Hans Krebs is a series of metabolic reactions that take place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. The whole cycle of Kreb is described in the following figure.
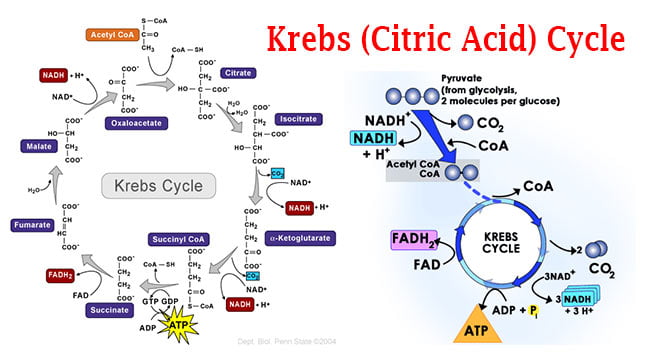 Source: microbiologyinfo.com
Source: microbiologyinfo.com
In this article we will discuss about the functions of the Krebs cycle explained with the help of diagrams. Krebs cycle The Krebs cycle also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle is one of the most important reaction sequences in biochemistry. In the first step of the citric acid cycle acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. Kreb Cycle Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle. Not only is this series of reactions responsible for most of the energy needs in complex organisms the molecules that are produced in these reactions can be used as building blocks for a large number of important processes.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The reactions which help in converting pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water in mitochondria are called the Krebs cycle. Y X W Z. Occurs in all the living organisms. Not only is this series of reactions responsible for most of the energy needs in complex organisms the molecules that are produced in these reactions can be used as building blocks for a large number of important processes. The whole cycle of Kreb is described in the following figure.
 Source: conceptdraw.com
Source: conceptdraw.com
Krebs Cycle is the second step of aerobic respiration in which pyruvate is oxidised completely into inorganic substances forming carbon dioxide. A 2 carbon acetylcoenzyme A from the link reaction combines with a 4 carbon molecule to produce a 6 carbon molecule 2. Every stage in each process is catalysed by a specific enzyme. Biology Draw Diagram And Explain Glycolysis And Krebs Cycle Using A Diagram Describe Glycolytic Pathway And Krebs Cycle Schematic Diagram Of Glycolysis The Kreb Cycle. The Krebs cycle also known as the citric acid cycle or TCA cycle is a series of reactions that take place in the mitochondria resulting in oxidation of acetyl CoA to release carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms that later lead to the formation of water.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The boxes in figure 5 represent substances in glycolysis the link reaction and the krebs cycle a Add to the diagram the number of carbon atoms present in one molecule of each compound. This 6 carbon molecule loses carbon dioxide and hydrogen to give a 4 carbon. The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalysed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced which generate ATP in the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle CAC also known as the TCA cycle tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates fats and proteinsThe TCA cycle is used by organisms that respire as opposed to organisms that ferment to generate energy either by anaerobic. KREBS CYCLE MADE SIMPLE - TCA Cycle Carbohydrate Metabolism Made Easy - YouTube.

This cycle describes a. Krebs cycle was named after Hans Krebs who postulated the detailed cycle. This cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. This cycle describes a. A 2 carbon acetylcoenzyme A from the link reaction combines with a 4 carbon molecule to produce a 6 carbon molecule 2.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Most of the released energy is converted into high energy bonds of ATP. This cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. Krebs made an outstanding contribution to the discovery of the operating mechanisms of this cycle which is also called tricarboxylic cycle or citric cycle owing to the participation of various tricarboxylic acids including citric acid. Biology Draw Diagram And Explain Glycolysis And Krebs Cycle Using A Diagram Describe Glycolytic Pathway And Krebs Cycle Schematic Diagram Of Glycolysis The Kreb Cycle. Occurs in all the living organisms.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
These organelles can be regarded as efficient low temperature furnaces where organic molecules are burnt with oxygen. These organelles can be regarded as efficient low temperature furnaces where organic molecules are burnt with oxygen. The Krebs cycle named after 1953 Nobel Prize winner and physiologist Hans Krebs is a series of metabolic reactions that take place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs cycle. The specific enzymes of the Krebs cycle are all located on the inner walls of the cristae of mitochondria subcellular organelles.
 Source: examfear.com
Source: examfear.com
Biology Draw Diagram And Explain Glycolysis And Krebs Cycle With Aid Of A Diagram Describe Glycolysis And Krebs Cycle Diagram To Draw On Biochemistry File. Put more simply this means that bacteria do not have the cellular machinery for the Krebs cycle so it limited to plants animals and fungi. The reactions which help in converting pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water in mitochondria are called the Krebs cycle. The whole cycle of Kreb is described in the following figure. These organelles can be regarded as efficient low temperature furnaces where organic molecules are burnt with oxygen.
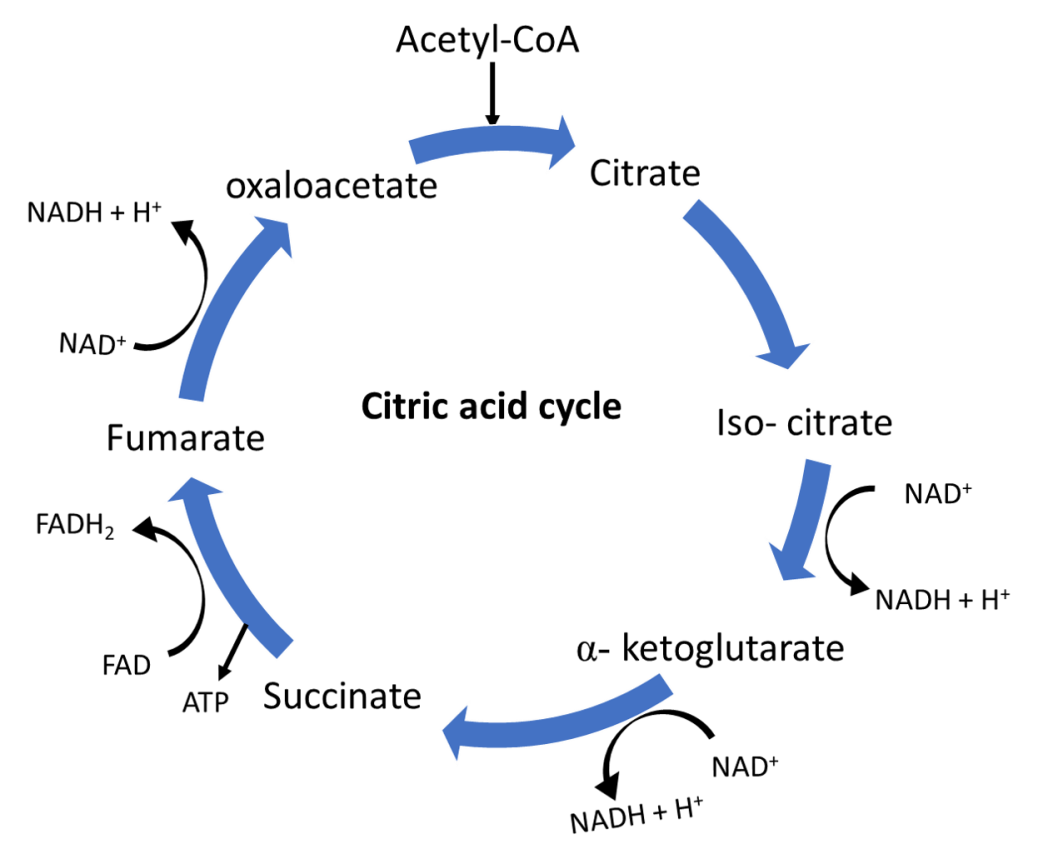 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
It involves the oxidative metabolism of acetyl units and serves as the main source of cellular energy mitochondria. Biology Draw Diagram And Explain Glycolysis And Krebs Cycle Using A Diagram Describe Glycolytic Pathway And Krebs Cycle Schematic Diagram Of Glycolysis The Kreb Cycle. This cycle describes a. The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme catalysed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix where acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced which generate ATP in the electron transport chain. This cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria.
 Source: brainly.in
Source: brainly.in
This 6 carbon molecule loses carbon dioxide and hydrogen to give a 4 carbon. Krebs cycle was named after Hans Krebs who postulated the detailed cycle. Krebs made an outstanding contribution to the discovery of the operating mechanisms of this cycle which is also called tricarboxylic cycle or citric cycle owing to the participation of various tricarboxylic acids including citric acid. The Krebs cycle also known as the citric acid cycle or TCA cycle is a series of reactions that take place in the mitochondria resulting in oxidation of acetyl CoA to release carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms that later lead to the formation of water. Not only is this series of reactions responsible for most of the energy needs in complex organisms the molecules that are produced in these reactions can be used as building blocks for a large number of important processes.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. Krebs made an outstanding contribution to the discovery of the operating mechanisms of this cycle which is also called tricarboxylic cycle or citric cycle owing to the participation of various tricarboxylic acids including citric acid. The citric acid cycle CAC also known as the TCA cycle tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates fats and proteinsThe TCA cycle is used by organisms that respire as opposed to organisms that ferment to generate energy either by anaerobic. Krebs Cycle is the second step of aerobic respiration in which pyruvate is oxidised completely into inorganic substances forming carbon dioxide. This cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. The boxes in figure 5 represent substances in glycolysis the link reaction and the krebs cycle a Add to the diagram the number of carbon atoms present in one molecule of each compound. Find an answer to your question Explain Krebs cycle with diagram badshahXmax badshahXmax 16032019 CBSE BOARD X Secondary School answered Explain Krebs cycle with diagram. The Krebs cycle involves a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that take place in the matrix of the mitochondria. Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs cycle.
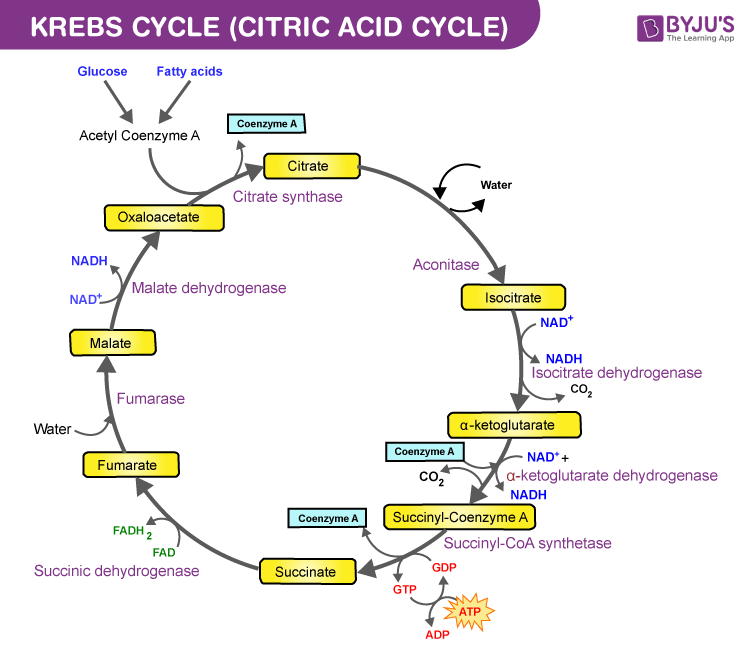 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Krebs cycle was named after Hans Krebs who postulated the detailed cycle. The specific enzymes of the Krebs cycle are all located on the inner walls of the cristae of mitochondria subcellular organelles. This cycle describes a. The Krebs cycle involves a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that take place in the matrix of the mitochondria. Y X W Z.
 Source: shaalaa.com
Source: shaalaa.com
Put more simply this means that bacteria do not have the cellular machinery for the Krebs cycle so it limited to plants animals and fungi. Most of the released energy is converted into high energy bonds of ATP. Occurs in all the living organisms. In the first reaction of the citric acid cycle acetyl CoA combines with the oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid. Krebs cycle was named after Hans Krebs who postulated the detailed cycle.
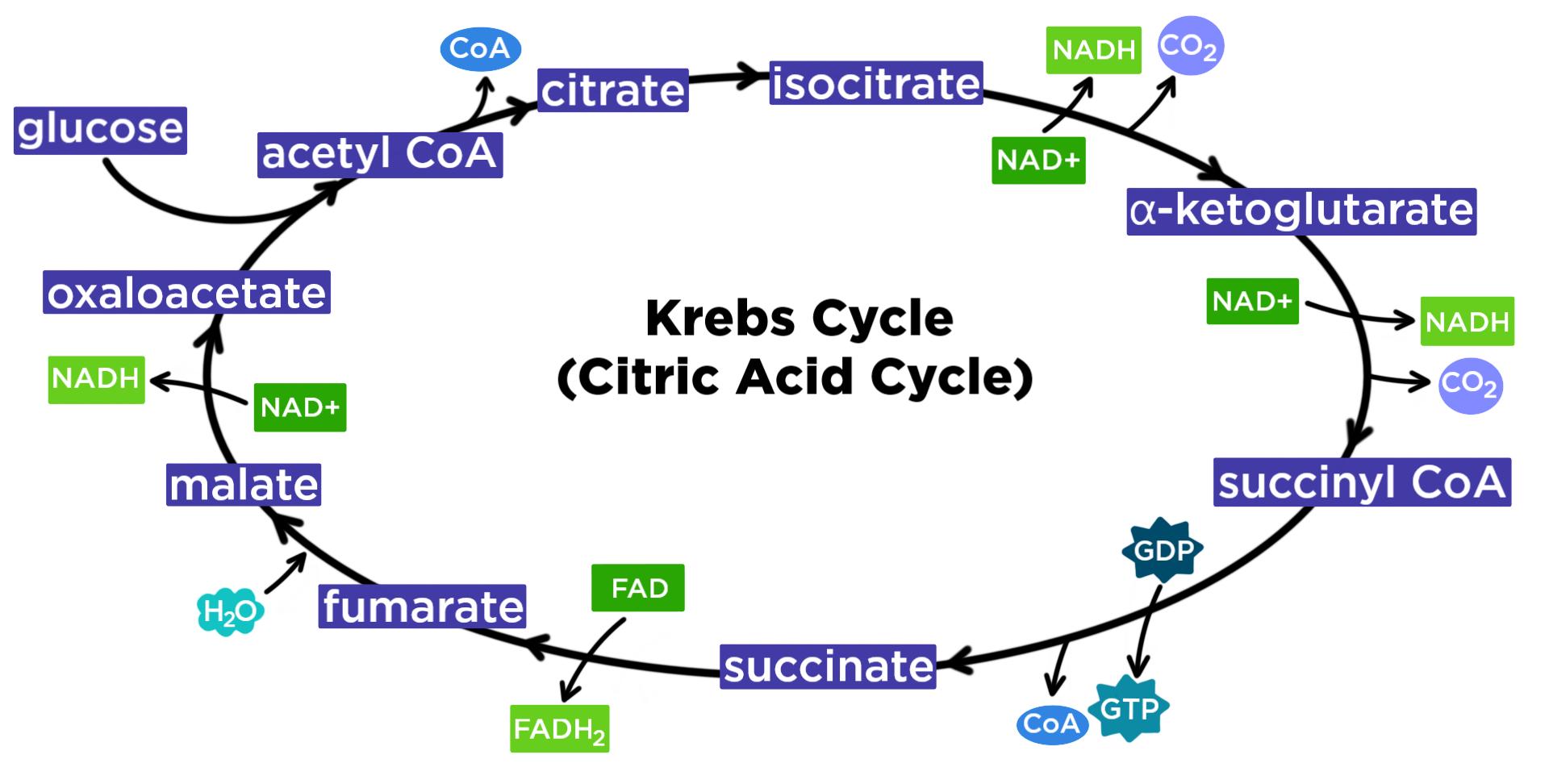 Source: expii.com
Source: expii.com
In the first reaction of the citric acid cycle acetyl CoA combines with the oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid. Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs cycle. In the first step of the citric acid cycle acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. Krebs made an outstanding contribution to the discovery of the operating mechanisms of this cycle which is also called tricarboxylic cycle or citric cycle owing to the participation of various tricarboxylic acids including citric acid. The Krebs cycle named after 1953 Nobel Prize winner and physiologist Hans Krebs is a series of metabolic reactions that take place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Biology Draw Diagram And Explain Glycolysis And Krebs Cycle Using A Diagram Describe Glycolytic Pathway And Krebs Cycle Schematic Diagram Of Glycolysis The Kreb Cycle. Order of carriers linked to sequence of reduction - reduced carriers cannot pass on electrons when inhibited 5. Krebs made an outstanding contribution to the discovery of the operating mechanisms of this cycle which is also called tricarboxylic cycle or citric cycle owing to the participation of various tricarboxylic acids including citric acid. Every stage in each process is catalysed by a specific enzyme. The Krebs cycle named after 1953 Nobel Prize winner and physiologist Hans Krebs is a series of metabolic reactions that take place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title explain krebs cycle with diagram by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.