Explain the antigen antibody reaction diagram
Home » Wallpapers » Explain the antigen antibody reaction diagramYour Explain the antigen antibody reaction diagram images are available in this site. Explain the antigen antibody reaction diagram are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Explain the antigen antibody reaction diagram files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for explain the antigen antibody reaction diagram pictures information linked to the explain the antigen antibody reaction diagram topic, you have come to the ideal site. Our site always gives you hints for viewing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
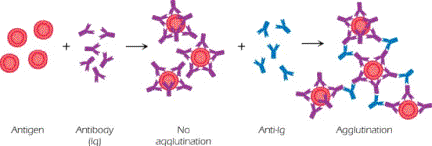
Explain The Antigen Antibody Reaction Diagram. All antibodies have at least two antigen binding sites represented as their Fab 2. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. However an antigen may not be able to induce the formation of an antibody and therefore may not be an immunogen. The antibody that cause agglutination are called agglutinins and particulate antigens aggregated are called agglutinogens.
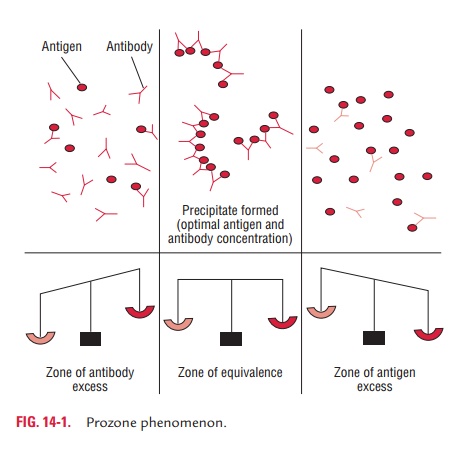 Precipitation Antigen Antibody Reactions From brainkart.com
Precipitation Antigen Antibody Reactions From brainkart.com
Such assays called particle agglutination PA are based on the ability of sera containing HIV antibodies to crosslink small particles containing HIV antigens on the surface. Antigens contain different antigenic determinants epitopeses that can elicit different types of antibodies In. Antigens could be anything like a pathogen or bacteria or fungi or even virus. The interaction between antigen and antibody occurs in two stages. Antibodies recognize molecular shapes epitopes on antigens. Centrifugation is the most widely used way to enhance antigenantibody reactions.
It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules such as pathogens and their chemical toxins.
They cause diseases or allergic reactions. Avidity is the strength of multiple interactions between antigen and antibody with multiple binding sites. Types of Antigen Antibody ReactionThe types of antigen antibody reactions are Precipitation Reaction Agglutination Reaction Complement Fixation ELISA Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay Immunofluorescence. The mechanism of antigen-antibody reactions has been an attractive subject for experimentation and speculation ever since the early days of immunology. Centrifugation is the most widely used way to enhance antigenantibody reactions. X-Ray crystallography studies of antigen-antibody interactions show that the antigenic determinant nestles in a cleft formed by the combining site of the antibody as illustrated in Figure 1.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
The precipitin reaction because of its technical simplicity has often been used for such studies without however any agreement as to the fundamental nature of the mechanism involved. Types of antigen– Antibody reactions in Antibody reactions in vivo 1. All immunogens are also antigens because they react with corresponding antibodies see illustration. Antigens could be anything like a pathogen or bacteria or fungi or even virus. Haemagglutination occurs when IgM antibodies react with their corresponding red cell antigens.
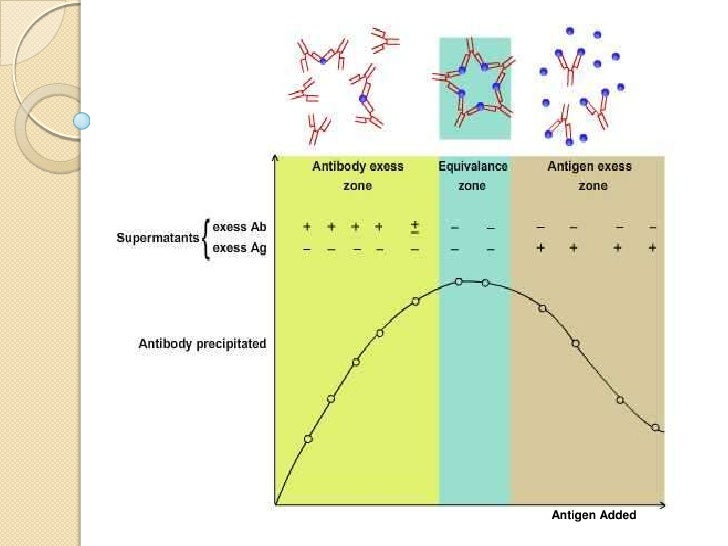 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The interactions between antigens and antibodies are known as antigenantibody reactions. A substance that induces the immune system to form a corresponding antibody is called an immunogen. Avidity is the strength of multiple interactions between antigen and antibody with multiple binding sites. Each antigen has a distinct surface feature or epitope. Antigen-Antibody Reactions To bridge the gap between basic immunology and antibody detection methods Module 3 we will now briefly review the nature of antigen-antibody reactions.
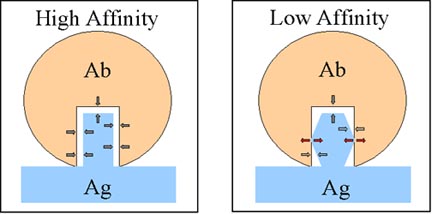 Source: microbiologybook.org
Source: microbiologybook.org
But we know that some antibodies IgM and IgA exist in secreted form as a multi-antibody complex. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules such as pathogens and their chemical toxins. Antigen-Antibody Reactions To bridge the gap between basic immunology and antibody detection methods Module 3 we will now briefly review the nature of antigen-antibody reactions. Macrophages engulf and destroy the clumped antigens. This is called agglutination.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
X-Ray crystallography studies of antigen-antibody interactions show that the antigenic determinant nestles in a cleft formed by the combining site of the antibody as illustrated in Figure 1. Antigens are molecules that bind to antibodies or T-cell receptors. When red blood called are agglutinated the reaction. Antigen Antibody Reaction Agglutination is defined as the formation of clumps of cells or inert particles by specific antibodies to surface antigenic components direct agglutination or to antigenic components adsorbed or chemically coupled to red cells or inert particles passive hemagglutination and passive agglutination respectively. Antigen-Antibody Reactions To bridge the gap between basic immunology and antibody detection methods Module 3 we will now briefly review the nature of antigen-antibody reactions.
 Source: www2.hawaii.edu
Source: www2.hawaii.edu
It is the clumping of a particular antigen and its antibody. All antibodies have at least two antigen binding sites represented as their Fab 2. Clumping of RBC due to antigen-antibody rxn. Antigens are substances that stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies. It provides flexible and useful method for semi quantitating of either antigen or antibody concentration.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The effects of antigen zygosity and red cell concentration are distinct. Certain organs are more commonly involved Read More. In the primary or initial stage non-covalent binding between the antigen and antibody produces small and soluble antigen-antibody complexes as a result of primary union. Antigens contain different antigenic determinants epitopeses that can elicit different types of antibodies In. The interactions between antigens and antibodies are known as antigenantibody reactions.
 Source: shaalaa.com
Source: shaalaa.com
The precipitin reaction because of its technical simplicity has often been used for such studies without however any agreement as to the fundamental nature of the mechanism involved. Antigens are molecules that bind to antibodies or T-cell receptors. This primary reaction has no visible effect and the reaction is rapid. Such assays called particle agglutination PA are based on the ability of sera containing HIV antibodies to crosslink small particles containing HIV antigens on the surface. Antibodies recognize molecular shapes epitopes on antigens.
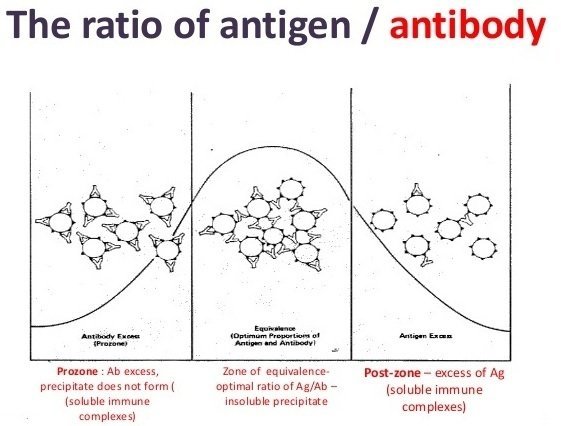 Source: microbeonline.com
Source: microbeonline.com
It is the clumping of a particular antigen and its antibody. For instance lipids and all low-molecular-weight substances are not immunogenic. Antigenantibody reactions occur in two stages. Antigens contain different antigenic determinants epitopeses that can elicit different types of antibodies In. Antigen-antibody complexes form only after the nuclear contents of a cell are released into the bloodstream during the normal course of cell death or as a result of inflammation.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
All antibodies have at least two antigen binding sites represented as their Fab 2. When red blood called are agglutinated the reaction. Antigen Antibody Reaction Agglutination is defined as the formation of clumps of cells or inert particles by specific antibodies to surface antigenic components direct agglutination or to antigenic components adsorbed or chemically coupled to red cells or inert particles passive hemagglutination and passive agglutination respectively. PA has advantages of sensitivity and relatively high inherent specificity because the presence of bivalent or multivalent reactions. They cause diseases or allergic reactions.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Thus there is a resultant effect of a specific response. Types of Antigen Antibody ReactionThe types of antigen antibody reactions are Precipitation Reaction Agglutination Reaction Complement Fixation ELISA Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay Immunofluorescence. Antigens are generally proteins. It is the clumping of a particular antigen and its antibody. Antigen-antibody interaction or antigen-antibody reaction is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction.
 Source: www2.hawaii.edu
Source: www2.hawaii.edu
Haptenss are partial antigens that require a carrier molecule to elicit an immune response eg medications. The interactions between antigens and antibodies are known as antigenantibody reactions. The reactions are highly specific and an antigen reacts only with antibodies produced by itself or with closely related antigens. Process by which cells or other particles adhere to each other to form clumps. The antibody that cause agglutination are called agglutinins and particulate antigens aggregated are called agglutinogens.
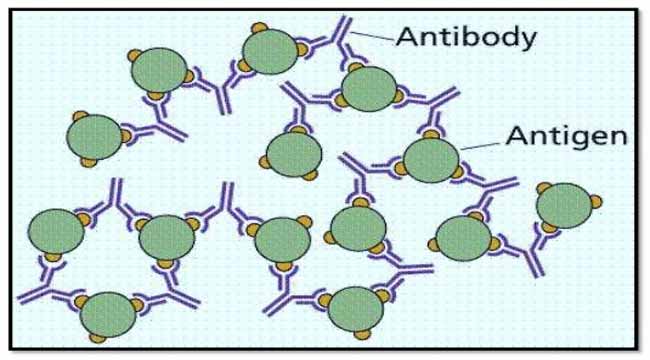 Source: microbenotes.com
Source: microbenotes.com
Avidity is the strength of multiple interactions between antigen and antibody with multiple binding sites. However an antigen may not be able to induce the formation of an antibody and therefore may not be an immunogen. Antigen-Antibody Reactions To bridge the gap between basic immunology and antibody detection methods Module 3 we will now briefly review the nature of antigen-antibody reactions. Allogeneic antigens. Even when the concentration of the antigen in the reaction system is equal in both cases and for this reason the concentration of the antigen-antibody complex too the number of antibodies per cell changes and favours homozygous cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The clumped antigens are not active. Antigen-Antibody Reactions To bridge the gap between basic immunology and antibody detection methods Module 3 we will now briefly review the nature of antigen-antibody reactions. PA has advantages of sensitivity and relatively high inherent specificity because the presence of bivalent or multivalent reactions. Antigens are molecules that bind to antibodies or T-cell receptors. They cause diseases or allergic reactions.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
For instance lipids and all low-molecular-weight substances are not immunogenic. Antigens are molecules that bind to antibodies or T-cell receptors. X-Ray crystallography studies of antigen-antibody interactions show that the antigenic determinant nestles in a cleft formed by the combining site of the antibody as illustrated in Figure 1. This primary reaction has no visible effect and the reaction is rapid. Each antigen has a distinct surface feature or epitope.
 Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
AGGLUTINATION Agglutination is an antigen antibody reaction where the antibody of serum causes the cellular antigen to adhere to one another to form clumps. Process by which cells or other particles adhere to each other to form clumps. They cause diseases or allergic reactions. AGGLUTINATION Agglutination is an antigen antibody reaction where the antibody of serum causes the cellular antigen to adhere to one another to form clumps. The reactions are highly specific and an antigen reacts only with antibodies produced by itself or with closely related antigens.
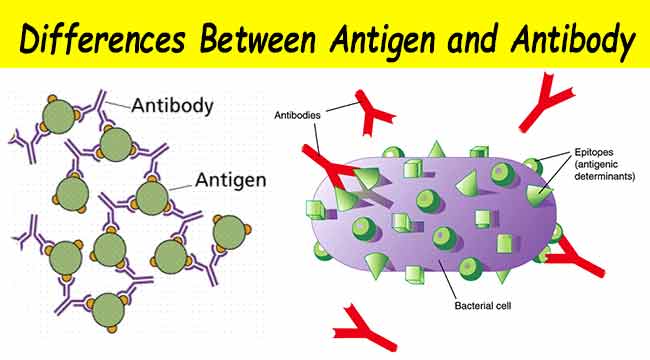 Source: microbiologyinfo.com
Source: microbiologyinfo.com
Each antigen has a distinct surface feature or epitope. All immunogens are also antigens because they react with corresponding antibodies see illustration. This primary reaction has no visible effect and the reaction is rapid. It provides flexible and useful method for semi quantitating of either antigen or antibody concentration. We explain both and how they work.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Antigens and antibodies work together in your immune system. Antigen-antibody complexes form only after the nuclear contents of a cell are released into the bloodstream during the normal course of cell death or as a result of inflammation. X-Ray crystallography studies of antigen-antibody interactions show that the antigenic determinant nestles in a cleft formed by the combining site of the antibody as illustrated in Figure 1. This is called agglutination. Types of Antigen Antibody ReactionThe types of antigen antibody reactions are Precipitation Reaction Agglutination Reaction Complement Fixation ELISA Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay Immunofluorescence.
 Source: www2.hawaii.edu
Source: www2.hawaii.edu
The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. The reaction will results in forming aggregate or. Antigens are substances that stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies. The interaction between antigen and antibody occurs in two stages. The antibody covers the toxic site of the antigen.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title explain the antigen antibody reaction diagram by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.